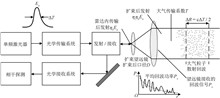
In light of the challenges posed by the requirement of numerous parameters calibration, the involvement of multiple metrology specialties, and the inadequacies in existing calibration methods for coherent Doppler wind lidar. Considering the characteristics of laser wind measurement, such as non⁃contact, high spatiotemporal resolution and large detection range, the method of "feature analysis and multi⁃method integration" is adopted to break through the difficulties of quantitative evaluation of controversial parameters such as wind speed, wind direction, maximum measurement distance and detection blind zone. The advantages, disadvantages and applicable conditions of three different wind speed calibration methods, namely the wind speed calibrations using a calibration turntable, the radio frequency signal simulation of Doppler frequency shift and using a standard anemometer, are analyzed. Moreover, the calibration turntable wind speed calibration method was improved to enhance the data reliability of the wind speed parameter calibration. Aiming at the difficult problem of wind direction calibration, the calibration method under different scanning modes is presented dialectically to improve its universality. Based on specific measurement cases, the calibration results of wind speed and wind direction are given, and the uncertainty analysis of wind speed and wind direction parameters are performed, effectively illustrating the feasibility of the calibration method. The research results provide standardized technical support for the precise detection of wind fields in such fields as meteorological observation, aviation safety, and new energy, and have positive significance for promoting the development of atmospheric remote sensing metrology technology.
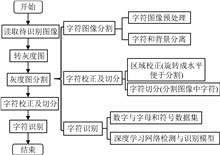
To address the inefficiency, error⁃proneness, and safety risks associated with traditional manual meter reading for pressure instruments, as well as the limited adaptability of automated meter⁃reading technologies based on sensors and 3D vision, this study integrates computer vision and artificial intelligence technologies to develop a metering system that combines data acquisition, real⁃time monitoring, and data analysis. By improving the fast region⁃convolutional neural network(Fast R⁃CNN) algorithm through data augmentation and a lightweight feature extraction network, the system optimizes instrument positioning accuracy in complex environments. Additionally, the DeepLabv3+ model is enhanced by incorporating channel attention and spatial attention mechanisms, along with a hybrid loss function, to improve character segmentation efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that the improved algorithm achieves an average positioning accuracy of 84% for instrument dial positioning and a mean Intersection over union of 78.6% for character segmentation in challenging industrial environments. Furthermore, the system reduces the time required for a single measurement by 85% compared to manual reading, confirming its high efficiency and strong adaptability. This research provides a scalable technical framework for intelligent monitoring of industrial equipment, offering the practical value for advancing digital and intelligent metering.